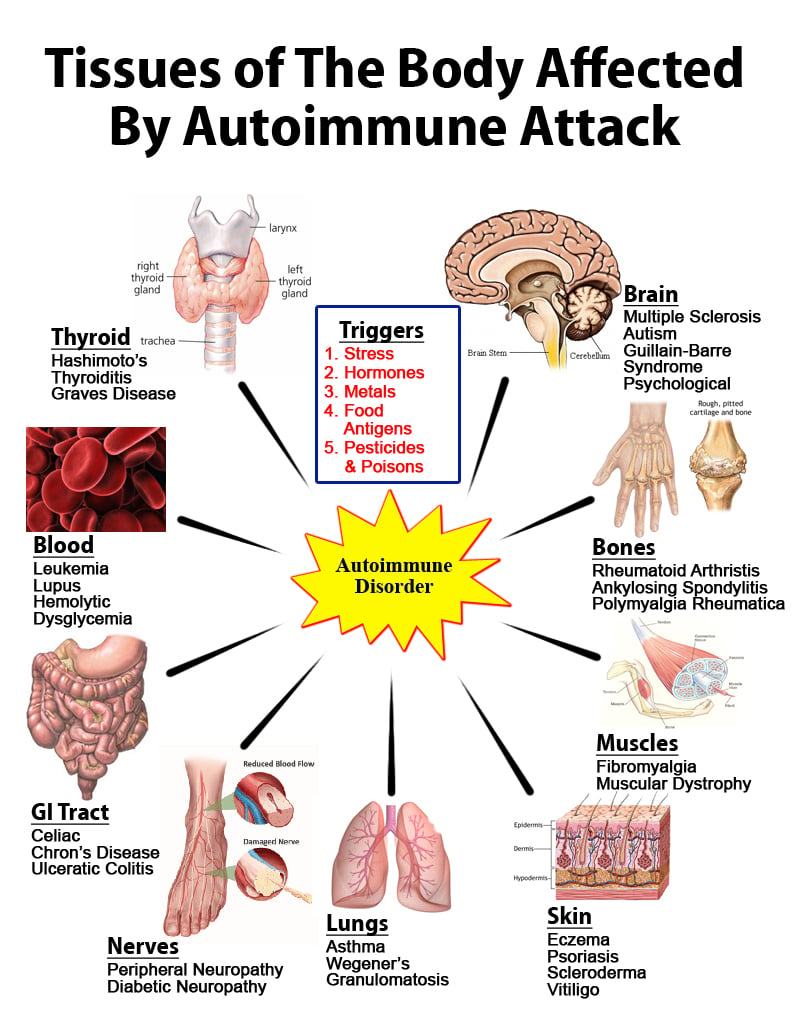
 An autoimmune disorder is a condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. Normally the immune system's white blood cells help protect the body from harmful substances, called antigens.In patients with an autoimmune disorder, the immune system can't tell the difference between healthy body tissue and antigens. Examples of autoimmune disorders are rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, addison's disease.
An autoimmune disorder is a condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. Normally the immune system's white blood cells help protect the body from harmful substances, called antigens.In patients with an autoimmune disorder, the immune system can't tell the difference between healthy body tissue and antigens. Examples of autoimmune disorders are rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, addison's disease.
Rsearchers from Purdue University discovered that Cells from one's own blood could be converted into a treatment for autoimmune diseases. Researcher has created a way to direct the differentiation of T-cells, a white blood cell that is a key player in the body's immune system.
The method involves, gathering of native T-cell from patient's blood, treated (suppressed) and then re-injected. The T cell collected is immature, from which all T-cells develop.
Treating autoimmune diseases without compromising a patient's immune system has been a big problem in the field. But, in the research, suppressive T-cells migrate to areas of inflammation and suppress the T-cells there without significantly lowering the number of T-cells in other areas of the body where they are needed for proper immune function.
In their research they suppressed T-cell in presence of hormone progesterone. They studied on mice and found that, about 500,000 suppressive T-cells are needed to have an effect on inflammation.
This discovery and his work have been detailed in papers in the Journal of Immunology and the European Journal of Immunology. They have also filed a patent based on their work.
No comments:
Post a Comment